|

1) CPC chromatograms
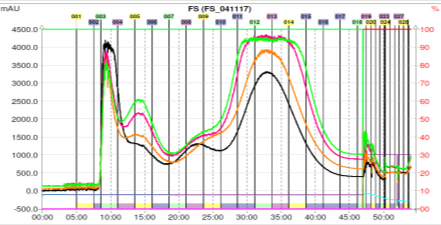
Fig. 1. CPC chromatogram of the n-butanol fraction (i) (1 g) of the fruits of F. suspensa. Fractions 11-16 were combined, dried and weighed.
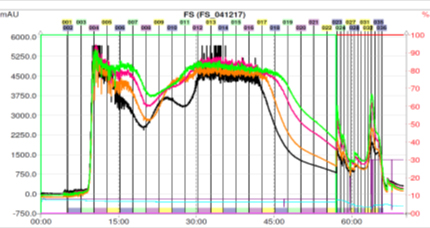
Fig. 2. CPC chromatogram of the n-butanol fraction (ii) (3 g) of the fruits of F. suspensa. Fractions 12-18 were combined, dried and weighed.

Fig. 3. CPC chromatogram of the n-butanol fraction (iii) (2.85g) of the fruits of F. suspensa. Fractions 13-21 were combined, dried and weighed.
Fig.1 ~ 3은 각각 1g, 3g, 2.85g injection 하여 정제한 결과이며 재현성 있는 결과로(target compound의 분획구간이 거의 같게 분리되었음을 볼 수 있다.) HPLC로는 분리하기 어려웠던 물질을 대량으로 분리해 낼 수 있었다.
2) 1H-NMR spectra of the n-BuOH fraction and forsythiaside A

Fig. 4. Comparison of 1H-NMR spectra of the n-BuOH fraction and the isolated forsythiaside A. * Denotes that the peaks from the residual n-BuOH in the fraction.
Fig.4 는 CPC로 분리한 분획을 NMR로 분석한 결과이며 n-BuOH 잔기를 제외하면 거의 일치하는 peak을 보여준다.
3) HPLC analysis of the fraction 13 obtained from the 1st run (the purest peak from the 1st run)
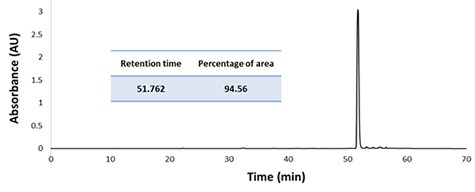
CPC 분획을 HPLC 조건에서 분리하였을 때 원하는 target compound인 forsythiaside A 만이 분리된 것을 볼 수 있었다.

본 연구에서는 CPC system을 이용하여 HPLC로는 정제가 어려웠던 천연물 분리 및 정제 기법을 제시하였다. HPLC 분석으로는 극성이 강한 천연물에 대해 분석이 어려우나 CPC 분석으로는 재현성 있는 정제분석이 가능하다는 것을 볼 수 있었다. 또한 컬럼이 필요없으며 용매소모량이 적어 매우 경제적인 분석 방법이라는 것을 알 수 있었다. CPC분석은 더욱 다양한 천연물 혹은 극성이 강한 화합물의 분석이나 Scale-up을 통해 수율을 높이고 싶거나 단일물질을 확인하고자 할 때에 매우 유용한 방법이라 할 수 있다.
|